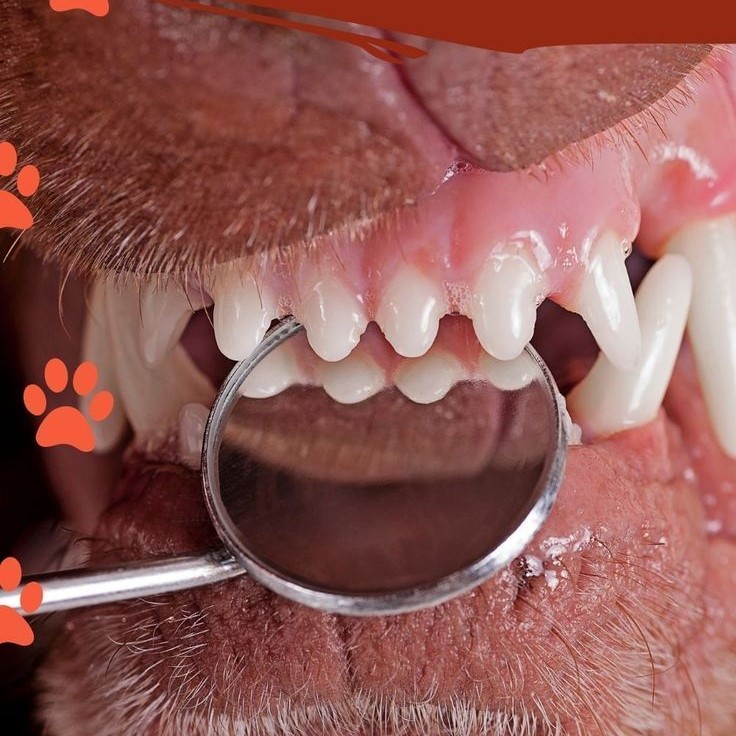
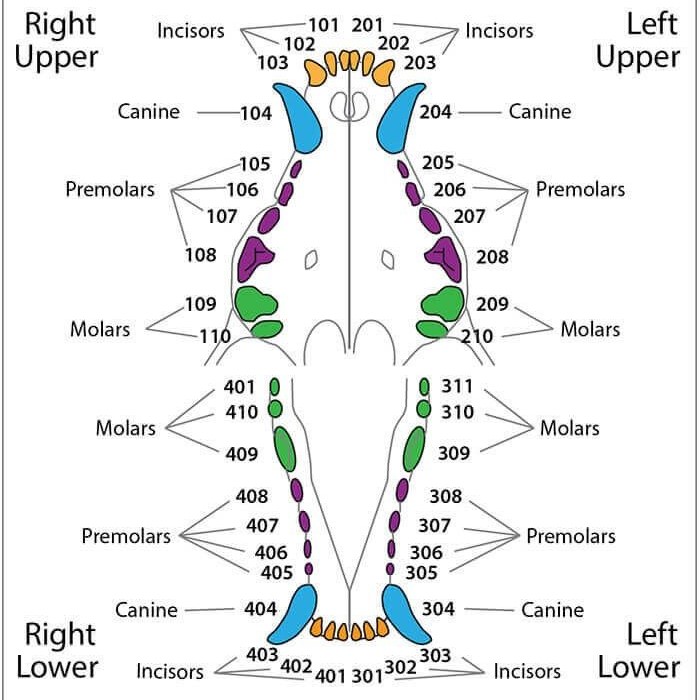
Overview of Dog Teeth Development
Understanding your dog’s teeth development is crucial for their overall health. Teeth play a role in chewing, eating, and even social behaviors. By observing tooth chart dog teeth age, you can estimate your dog’s age, especially in puppies. Additionally, tracking dental development helps in ensuring proper care and addressing any issues early.
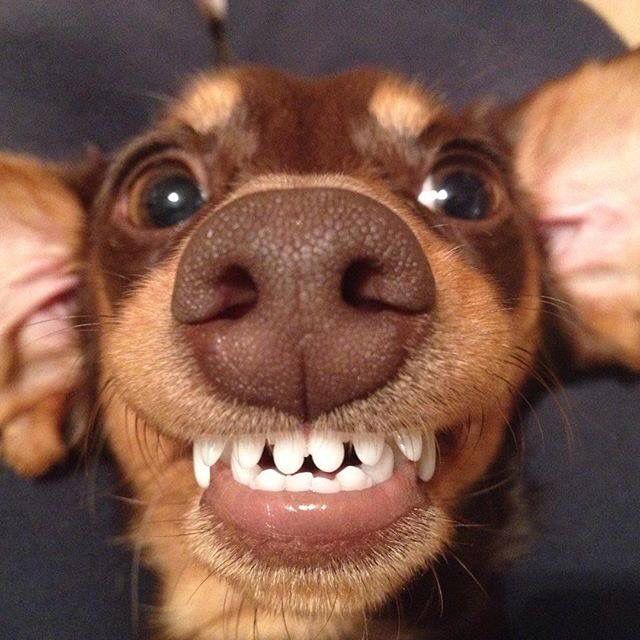

Why Understanding Dog Teeth Development is Important
Dogs, like humans, go through several stages of teeth growth. Knowing these stages benefits owners in multiple ways:
- Health Monitoring: Early detection of dental issues, such as misaligned teeth or gum problems, becomes easier.
- Age Estimation: A dog’s teeth can help approximate their age, especially for adopted pets.
- Behavior Management: Teething puppies may chew excessively, and understanding this helps manage behaviors effectively.
By understanding teeth growth, dog owners can ensure their pet’s oral health and overall wellbeing.
General Timeline for Puppy and Adult Teeth Eruption
Here’s an overview of the general timeline for dog teeth eruption:
- First Few Weeks: Puppies are born without visible teeth.
- 2-4 Weeks Old: Baby teeth (also called milk teeth) start appearing. Puppies usually get 28 of these.
- 3-4 Months Old: Puppies begin losing baby teeth as adult teeth emerge.
- 5-7 Months Old: Most adult teeth fully erupt by this stage. Dogs have 42 permanent teeth.
Understanding these timelines helps you monitor your dog’s dental development more effectively. Regular checks can ensure the proper growth of teeth and address any potential issues early.
Puppy Teeth: What to Expect
Puppy teeth growth is an essential part of their early development. Understanding this process helps owners care for their puppy’s dental needs. Puppies go through significant changes in their mouths during their first few months.
Stages of Puppy Tooth Development
Puppies experience distinct stages of tooth development. These stages give insight into their growth:
- Birth to 2 Weeks: Puppies are born toothless. Their gums are soft and undeveloped.
- 2-4 Weeks: Baby teeth, also called milk teeth, begin to emerge. A full set of 28 baby teeth will form.
- 3-4 Months: Puppies start losing baby teeth. This process helps adult teeth grow in.
- 5-7 Months: All adult teeth usually erupt. By this age, puppies should have 42 permanent teeth.
Monitoring these stages ensures proper growth and prevents dental issues.
Signs of Teething in Puppies
Teething can be uncomfortable for puppies. Here are common signs to watch for:
- Chewing: Puppies may chew furniture, toys, or anything within reach. It’s a natural instinct.
- Drooling: Increased drooling can occur as adult teeth push through gums.
- Irritability: Puppies might seem fussy or restless during teething.
- Swollen Gums: Gums may appear red or inflamed as new teeth emerge.
- Decreased Appetite: Pain from teething may lead to reduced eating temporarily.
Providing appropriate teething toys can help soothe their discomfort. Regular checks ensure their teeth develop correctly.
Understanding puppy teeth growth and teething signs allows owners to support their pet’s dental health.
Adult Dog Teeth Timeline
As dogs grow, their teeth development marks important milestones. Tracking these changes can help owners monitor oral health and estimate age accurately.
When Do Puppies Lose Their Baby Teeth?
Puppies typically start losing their baby teeth between 12 to 16 weeks of age. Baby teeth, also called milk teeth, loosen as permanent teeth begin pushing through. This process usually continues until the puppy reaches 6 months of age.
Here’s how the timeline looks:
- 12 to 16 Weeks: Front incisors start falling out, followed by canine teeth.
- 16 to 20 Weeks: Premolars and molars begin replacing baby counterparts.
- 6 Months: Most puppies have lost all baby teeth and have nearly all permanent teeth.
During this time, teething may cause discomfort. Providing chew toys can relieve pain and prevent chewing on household items.
Age Milestones for Permanent Teeth
Once baby teeth are gone, adult teeth emerge. By observing the shape and wear of these teeth, you can estimate your dog’s age at various stages.
- 6 to 7 Months: Dogs usually have their full set of 42 permanent teeth.
- 1 Year Old: Teeth appear clean and white, with minimal chewing damage.
- 3 Years Old: Mild tartar buildup begins, especially on molars and premolars.
- 5 Years Old: Tartar is more visible, and teeth may show wear from chewing.
- 10+ Years Old: Teeth show signs of wear, discoloration, and possible loss due to aging.
Understanding these milestones helps owners identify potential oral health issues early on. Regular dental checks ensure your dog’s teeth stay healthy throughout their life.
Using a Tooth Chart to Determine Dog Age
Dog teeth charts are useful tools for estimating a dog’s age. They provide details on how teeth change over time. Owners can easily compare their dog’s teeth with expected age-based growth and wear patterns.
How to Read a Dog Teeth Chart
Reading a tooth chart dog teeth age involves understanding the typical development stages:
- Puppy Teeth (Birth to 6 Months): Look for baby teeth and their loss as adult teeth emerge.
- Young Adult Teeth (6 Months to 1 Year): Permanent teeth are clean, white, and damage-free.
- Middle-Aged Teeth (1 to 5 Years): Mild tartar buildup is visible, especially on molars and premolars.
- Senior Teeth (5+ Years): Teeth show wear and discoloration; some may even be missing.
The chart serves as a reference to compare your dog’s teeth condition to standard timelines. By matching their teeth appearance to the tooth chart dog teeth age, you can estimate age more accurately.
Correlating Teeth Wear to Dog Age
Teeth wear is a reliable indicator for gauging a dog’s age. Here’s how:
- Clean and Sharp Teeth (Under 1 Year): Teeth are pristine with no signs of wear.
- Minor Wear and Tartar (1–3 Years): Small tartar buildup and slight chewing marks may appear.
- Visible Tartar and Wear (4–10 Years): These are signs of regular chewing and dental aging.
- Worn or Missing Teeth (10+ Years): Aging results in some teeth loss and significant discoloration.
Using teeth wear patterns along with a tooth chart dog teeth age provides a more accurate age estimate. Regular dental exams will further validate these observations.
Common Dental Issues in Dogs
Dogs can experience various dental problems as they age. Being aware of these issues helps prevent severe complications and ensures better oral health. Regular observation and care are essential for addressing dental challenges promptly.
Signs of Dental Problems Related to Aging
Aging dogs often exhibit specific signs of dental issues. Recognizing these symptoms is critical for timely intervention:
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath may signal plaque buildup or gum disease.
- Tartar Buildup: Yellow or brown tartar on teeth is common in older dogs.
- Swollen or Bleeding Gums: Inflamed gums can indicate gingivitis or periodontal disease.
- Loose or Missing Teeth: Tooth loss occurs more frequently with advanced dental issues.
- Difficulty Eating: Dogs may chew less or drop food due to oral discomfort.
- Pawing at the Mouth: This could suggest pain caused by dental problems.
If you notice any of these signs, consult a veterinarian for an examination and treatment.
Importance of Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups are vital for maintaining your dog’s oral health. Here’s why they matter:
Early Detection of Problems
- Timely Assessments: Regular dental checkups provide veterinarians with the opportunity to assess your dog’s oral health thoroughly. This proactive approach ensures that any potential issues can be identified at an early stage.
- Identification of Gum Disease: Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is a common dental issue in dogs. Checkups can help identify signs of inflammation, tartar buildup, and other early symptoms before they progress to more severe stages that require invasive treatments.
- Detection of Infections: Infections in the mouth can lead to serious health issues if left untreated. Routine evaluations enable veterinarians to spot infections early, allowing for prompt treatment that prevents complications.
- Overall Health Monitoring: Oral health is closely linked to overall health. By catching dental problems early, veterinarians can also monitor for associated issues that may arise in other parts of the body.
Preventative Care
- Professional Cleanings: One of the primary benefits of dental checkups is the opportunity for professional cleanings. These cleanings help remove tartar and plaque buildup that regular brushing may not entirely eliminate.
- Education on Oral Hygiene: During check-ups, veterinarians can educate pet owners about proper dental care practices at home, including brushing techniques, appropriate products, and the importance of regular cleaning routines.
- Preventing Future Problems: By maintaining your dog’s dental hygiene and addressing issues before they escalate, you significantly reduce the chances of future dental problems. This preventative care approach can save time, money, and discomfort for both the pet and the owner.
- Customized Care Plans: A veterinarian can create a tailored dental care plan for your dog, considering their age, breed, and specific needs. This personalized approach ensures that your dog receives the best preventative care.
Pain Relief
- Alleviation of Discomfort: Dental issues in dogs can often lead to pain and discomfort. Regular checkups allow for the early treatment of these conditions, ensuring that your dog remains pain-free and comfortable in their daily activities.
- Preventing Chronic Pain: Untreated dental problems can result in chronic pain conditions, which are often harder to manage. By addressing dental issues promptly, you can help prevent long-lasting pain that affects your dog’s quality of life.
- Behavioral Improvements: Dogs experiencing dental pain may exhibit changes in behavior, such as reluctance to eat, decreased activity, or aggression. Keeping their teeth and gums healthy can lead to more positive behavior and a better relationship with family members.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Regular dental checkups that lead to early treatment help maintain your dog’s overall well-being, allowing them to enjoy life to the fullest without the hindrance of dental pain.
Improved Lifespan
- Link Between Oral and Systemic Health: Research indicates a significant correlation between oral health and overall health in dogs. Maintaining a healthy mouth minimizes the risk of bacteria entering the bloodstream and causing infections in vital organs such as the heart, liver, and kidneys.
- Reduced Risk of Severe Diseases: By preventing oral diseases, you also minimize the risk of conditions like endocarditis (an infection of the heart lining) or other systemic illnesses, which can have life-threatening consequences.
- Promoting Longevity: Healthy dental hygiene practices can contribute to a longer, healthier life for your dog. A focus on oral health often correlates with an increased lifespan, as dogs with fewer health complications tend to live longer lives.
- Routine Monitoring for Lifespan Extension: Regular veterinary checkups provide ongoing monitoring of your dog’s oral health status, creating opportunities to address any emerging issues that could potentially shorten their lifespan.
Aim for annual dental exams, or more frequent visits for older dogs. Discuss your dog‘s oral hygiene needs with your vet to ensure proper care.
Tips for Maintaining Your Dog’s Dental Health
Taking care of your dog’s teeth is essential for their overall health. Proper dental care prevents problems and ensures your dog stays happy and healthy.
Dental Care at Different Life Stages
Dogs require tailored dental care at each life stage to maintain oral health:
- Puppies (Up to 6 Months):
- Begin dental care early. Use soft toothbrushes and puppy-safe toothpaste.
- Provide chew toys to soothe teething discomfort.
- Young Adults (6 Months to 2 Years):
- Brush their teeth daily to prevent plaque buildup.
- Schedule a professional dental cleaning if needed.
- Adults (2 to 5 Years):
- Continue regular brushing and dental checkups.
- Check for signs of mild tartar buildup.
- Seniors (5+ Years):
- Monitor for gum disease, missing teeth, and wear.
- Ensure annual dental exams for comprehensive care.
Each stage of life requires focused attention to keep teeth healthy and strong.
Tools and Practices for Proper Dog Oral Hygiene
Maintaining your dog’s oral hygiene involves using effective tools and regular practices:
- Brushes and Toothpaste:
- Use dog-specific toothpaste and soft-bristled brushes.
- Avoid human toothpaste to prevent harm.
- Dental Chews and Toys:
- Offer toys and treats designed to reduce plaque and tartar.
- Monitor for signs of excessive wear on teeth.
- Dietary Measures:
- Feed your dog crunchy kibble to help reduce tartar.
- Avoid sugary treats that promote plaque.
- Professional Dental Cleaning:
- Schedule professional cleanings when plaque buildup is severe.
- Follow veterinary advice for ongoing care.
- Daily Checking Routine:
- Examine their teeth for discoloration, cracks, or swollen gums.
- Brush at least three times a week for best results.
Using the right tools and maintaining a consistent routine strengthens your dog’s oral health. Regular efforts ensure fewer dental issues and a longer, healthier life for your pet.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dog Teeth and Age
Dog teeth and their wear patterns offer valuable clues about age. However, there are limitations and exceptions. Let’s address common questions surrounding this topic.
How Accurate is a Dog Teeth Chart for Determining Age?
Dog teeth charts provide a useful age estimation tool. They map teeth development to specific age ranges. Factors like tartar buildup and teeth wear help estimate a dog’s life stage.
However, accuracy depends on proper observation. Environmental factors and care influence teeth conditions. Dogs with consistent dental care may show fewer signs of tartar or wear.
For puppies, teeth eruption timelines are predictable. For adult dogs, teeth wear varies based on diet and chewing habits.
Consider teeth tooth chart dog teeth age as estimates rather than exact indicators. Combined with veterinarian assessments, they provide better age accuracy.
What if My Dog’s Teeth Don’t Match the Expected Timeline?
Several factors can cause deviations in teeth development:
- Breed Differences: Smaller or larger breeds may have unique teeth growth rates.
- Diet: Soft diets reduce wear compared to crunchy kibble.
- Health Issues: Gum disease or malnutrition can impact teeth appearance.
- Dental Care: Dogs receiving regular dental cleanings have less tartar and wear.
Consult a vet for unexpected teeth conditions. They can perform a thorough examination to identify abnormalities.
Teeth alone aren’t always enough to estimate a dog’s age. Combine teeth observations with other aging signs like eye clarity, muscle tone, and behavior changes.
By addressing these questions, dog owners can better understand and monitor their pet’s dental health and age estimation.